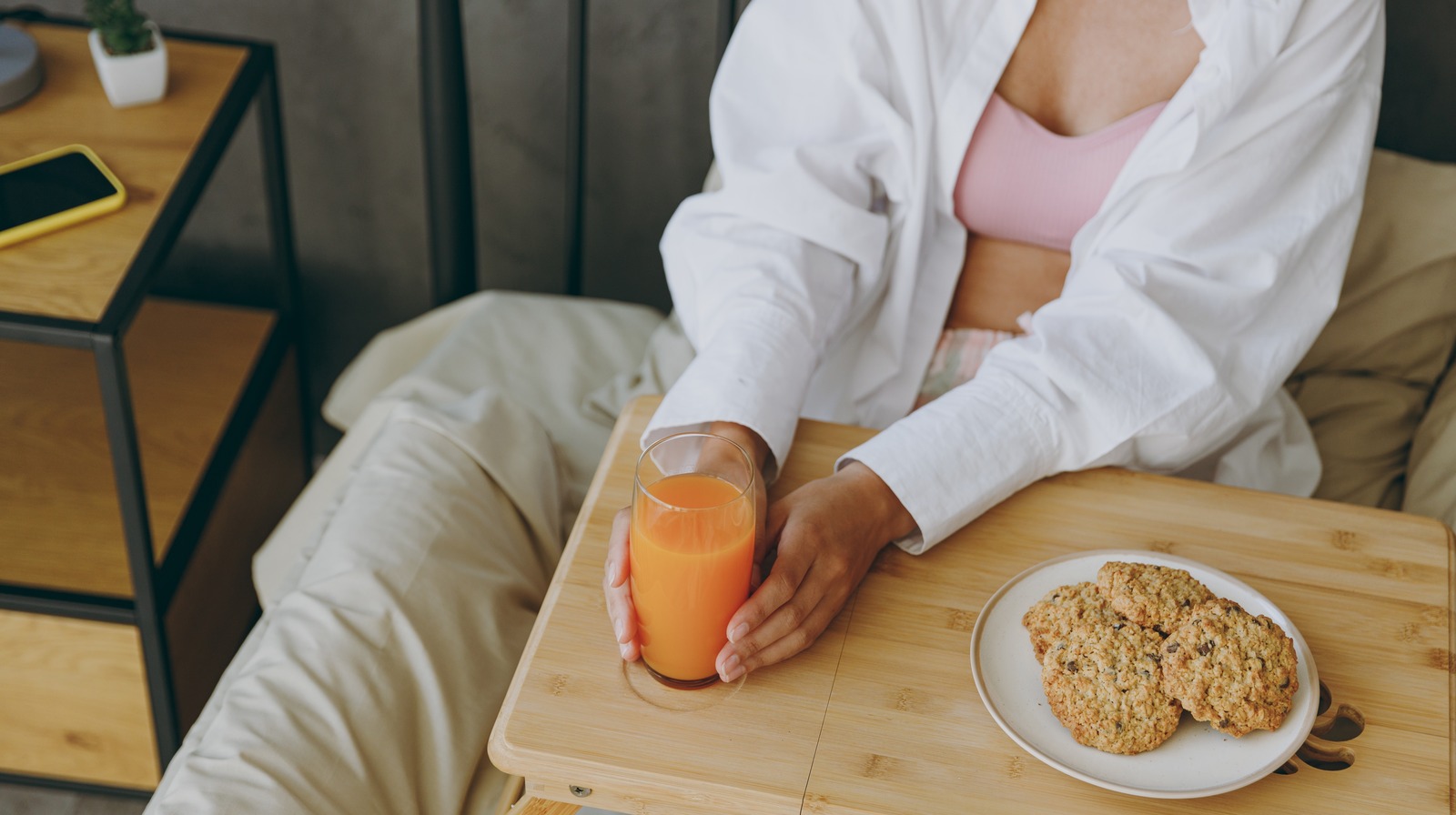
For starters, consuming a high-sugar diet can lead to a vicious cycle that results in poor sleep quality. Spikes and sharp drops in blood sugar levels brought on by high sugar consumption can throw your system out of whack and lead to lethargy and hunger. According to a clinical psychologist who specializes in sleep disorders, Dr. Michael Breus (via The Guardian), this is where the domino effect starts. You may end up feeling hungry at night too, and reaching for more sugary treats to curb that hunger can cause further spikes in blood sugar levels and mess with your sleep.
Your body interprets sugar as energy and prepares you for activity, when in fact, what you should be doing is getting ready to wind down. Poor sleep brought on by this overstimulation can further perpetuate out-of-control hunger cues and lead to more sugar cravings, per the clinical psychologist.
Additionally, blood sugar increases, and the resulting crashes, can also lead to thirst and the need to use the bathroom at night. This can result in disturbed sleep as well. Plus, “sugar uses up a lot of magnesium [magnesium helps regulate blood sugar], which you need for sleep,” per nutritional therapist Charlotte Watts and co-author of “Good Mood Food” (via The Guardian). Magnesium regulates gamma-aminobutyric acid, or GABA, the neurotransmitter responsible for calming the nervous system. It also promotes muscle relaxation and melatonin production, while decreasing the stress hormone cortisol. All of these functions aid sleep. There are more roundabout effects of sugar on sleep too.